Not everyone knows what arthrosis is, because of this, people get confused in treatment methods and do not understand the principles of diagnosis of pathology.Arthrosis is a severe dystrophic violation that provokes the lesion of cartilage tissues in the intraarticular cavity.The complexity of therapy is associated with the irreversibility of processes, a complete cure in the framework of modern medicine cannot be achieved, but the severity of the symptoms can be reduced and the progression of the pathology can slow down.With proper treatment, a person continues the usual lifestyle for a long time.
What is arthrosis?
Similarly, it is simpler that for the disease arthrosis is a disease of the joints that provokes the restriction of the amplitude of movement and pain.At the first stage of damage, there are no manifestations, have slight severity and washed off.Gradually, pathology progresses, this is facilitated by age -related changes in the body, stress, injuries, etc. According to statistics, about 80% of the population over 60 years old from arthrosis.
The arthrosis of the joint develops for a long time, initially only affects the hyalin cartilage, then spreads to the bones, involves the synovial shell, muscles and the entire joint capsule.At the first or early stage of arthrosis, the lesion is slightly manifested: small pains after hard work, swelling, redness of the skin.Due to ignoring uncomfortable sensations, the joint is deformed, inflamed, brings severe pain, their peak falls in the morning.The disease is characterized by the disappearance of pain after the development of the joint.If not treated, a person loses the mobility of the joint completely.
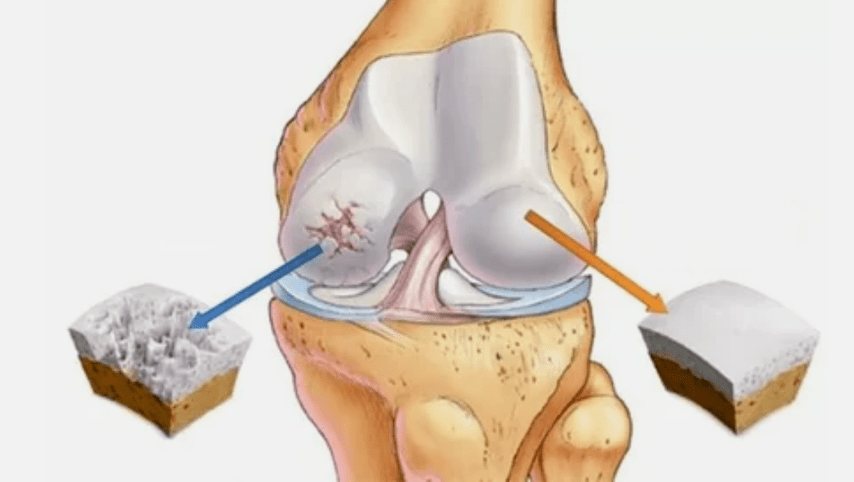
There is a primary and secondary form of arthrosis.Pseudo-arthrosis (neoartrosis) is also distinguished- not many people know what it is, since it is formed less often than other varieties.Neoarthrosis is a false joint, so cartilage tissue increases in an unusual place where damage was obtained.It is difficult to treat, mainly surgically.
There is a pathology due to disorders of regenerative function, immunity or mechanical damage.Due to various causes of cartilage, it becomes thinner.In normal condition, cartilage fabric receives sufficient nutrition for recovery, but after excessive physical exertion or due to a violation of metabolic processes, the fabrics do not have time to regenerate.At the first stage, joint mobility remains.Having considered what arthrosis is as a definition, it is worth deepening in more detail into the development of pathology.
The mechanism of development of arthrosis, its types
Many varieties of arthrosis develop according to a similar scheme:
- The primary lesion affects the hyaline cartilage.In case of circulatory disorders, pathological power deterioration occurs.It is the first step or cause, which may occur arthrosis.
- Hyalin coating pathologies.The thinning of the cartilage leads to the replacement of its pathological tissues - bone structures.
- Anomalous growths appear on cartilage - osteophytes.
- The arising violation of the natural anatomy of the cartilage and bones provokes the overload of healthy areas of cartilage.The destruction of articular tissues without treatment is constantly progressing and lead to disability.
When the degree of disease increases, pathological processes are still aggravated.In the end, all hyalin cartilage is destroyed.
The last degree of the disease leads to:
- involvement in the pathological process of bones, under and above the cartilaginous surfaces;
- irritation of a joint shell, limiting mobility, which leads to disability of 2 degrees;
- increased capsule density;
- Reducing the gap in the gap of the joint, which becomes noticeable in the picture.The stage of the violation is determined by the diagnostic-tantgenologist.The patient feels the complexity or inability to completely straighten and bend the limb;
- joint deformation, cartilage acquires an irregular shape, provoking curvature;
- deterioration in the patient's condition with complete destruction of joint.
Stages of arthrosis
Joint disease has 3 stages of development:
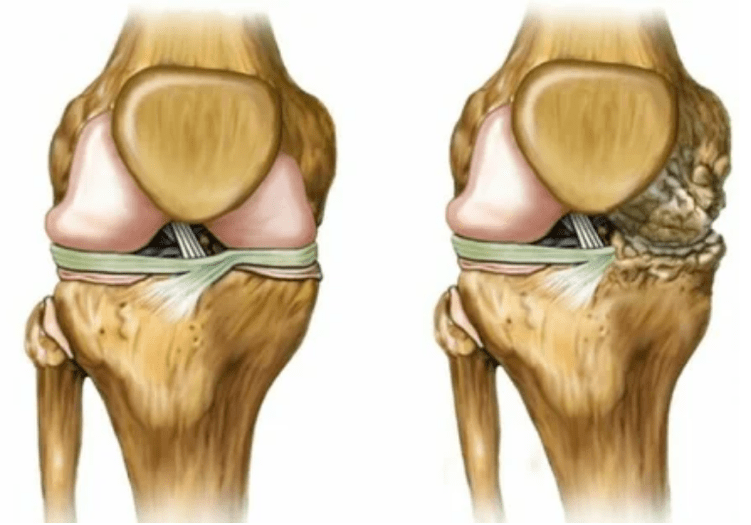
- 1 degree.Morphological disorders have already begun, but they are not yet noticeable.Pathology mainly affects the condition of synovial fluid, which worse supplies cartilage tissues with nutrient components, reducing the strength of the cartilage.The load on the joints provokes inflammation and pain.
- Stage 2.Due to the supply deficiency, the necessary cartridges are destroyed, bone growths are formed on the surface of the cartilage.The pains acquire a more pronounced character, intensify after a long rest, are eliminated by small physical labor.Pain is accompanied by inflammation.The muscles are stretched, which leads to weak or average impaired motor functions.
- 3 degree.Often there are pains, it is difficult to move the limb due to changes in the joint.The lesions are extensive, become noticeable to the naked look.The deformation of the joint site occurs, the affected area swells and becomes red.The limb axis is disturbed, which leads to the complexity of movement.Pathological changes provoke shortening the ligaments.Subluishes and contractures appear.The adjacent muscles are shortened or stretched, from which the contractile function is weakened.
Causes and risk factors for the development of arthrosis
The causes of arthrosis of the joints differ depending on the form of pathology.Deforming arthrosis of the elbow joint, ankle joint and shoulder arthrosis sometimes develop without noticeable causes, it is possible to detect them with a doctor, a specialist in rheumatology.If the problem was not preceded by visible pathologies, the disease is called primary.The secondary form of violation is mainly diagnosed, it can provoke various states.
The main reasons for development:
- Mechanical damage: dislocations, fractures, stretching, meniscus injuries;
- a number of endocrine disorders associated with malfunctions in the work of immunity;
- metabolism pathologies;
- dysplasia (congenital anomalies of articular tissues);
- suffered inflammation of the joints;
- pathologies leading to high mobility of the joints and weakening of the ligaments.
Patients with arthrosis most often encountered a disease due to predisposing factors:
- age -related changes;
- Light weight and increased BMI.High load on the joint leads to rapid joint wear;
- lack of beneficial substances;
- Excessive load on the joints.The reason is intense training, sports, hard physical work;
- difficult working conditions or an incorrect approach to sports.If there is a history of a genetic tendency to damage, joint injuries or similar diseases, it is important to adhere to a special training program, avoiding traumatic and difficult exercises;
- The postoperative period of recovery or transmitted complex operations associated with the excision of a large share of affected fabrics.Such states negatively affect the smoothness and strength of the cartilage, the load should be minimized on them;
- genetic tendency, arthrosis is more often diagnosed in patients who have relatives with the same pathology;
- The stage of postmenopause, occurs in women for about 50 years, is associated with changes in the endocrine system;
- the destructive effect of toxins;
- poor environmental situation in the region of residence;
- frequent damage to the joint, sometimes microcracks do not appear for a long time;
- hypothermia;
- Pathology of the lumbar and cervical part of the spine.
Primary arthrosis

Primary arthrosis is formed independently, that is, without the influence of any internal or external causes.The defeat develops through the hyalin cartilage quite slowly.It is rarely diagnosed, it accounts for only 3-5% of all cases.
Secondary arthrosis
Secondary arthrosis is most often detected by an order of 95-96% of cases.They are provoked by any of the above pathologies.
Signs and symptoms of arthrosis
The manifestations of the disease differ little depending on localization, more often the signs are reflected on the knees, shoulder and hip joints, due to high load.
Mostly complaints come down to:
- pain.They have low severity at the initial stage, with aggravation of the state of sensation intensify.Initially, the joints hurt only after waking up, after a light warm -up, sensations disappear.Over time, the pains appear at night, they greatly disturb during and after prolonged walking, running, etc. At the last stage, the pain syndrome pursues a person all the time;
- limited amplitude of movements.The stiffness of actions indicates anatomical changes in the structure.At first it manifests itself in the morning, then daily movements are limited.In order not to provoke aggravation of the condition, the work must be diverse and light, otherwise the patient will not be able to unclench and squeeze the limb over time.Over time, there is a risk of contracting, from which a person loses motor ability;
- Crown during movements - it belongs to the nonspecific manifestations of arthrosis.The disease is characterized by the occurrence of crunch in a single joint (except for polyarthrosis), accompanied by a discomfort, pain, and limited actions.The nature of the current is wave -like - at first it manifests itself weakly, gradually intensifies, but at 3 stages disappears;
- swelling with redness.It is localized near the diseased joint, this indicates an inflammatory process and progression of the disease.The doctor understands that the synovial shell is affected, this provokes the accumulation of fluid and increased pain;
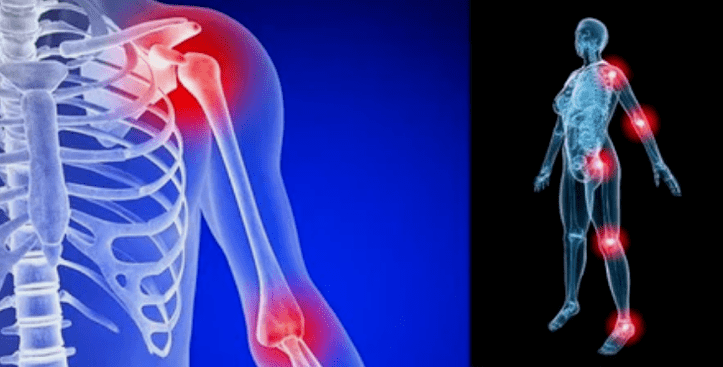 limb deformations.Appears in a neglected form of the disease, indicates the complete destruction of cartilage tissue and the appearance of osteophytes.In this state, pressure on the joints on top and below increases, from which curvature can affect the entire limb.
limb deformations.Appears in a neglected form of the disease, indicates the complete destruction of cartilage tissue and the appearance of osteophytes.In this state, pressure on the joints on top and below increases, from which curvature can affect the entire limb.
It is important to remember that the deformation of the bones on the leg is often confused with the corn.The symptom is poorly hazardous only at first glance, but leads to serious consequences.
Complications
Initially, conservative methods of therapy are used for treatment.If they are ineffective or the patient ignored the doctor’s recommendations, there is a risk of consequences.
Possible complications:
- The joint is completely destroyed;
- The limb is immobilized, any movements become extremely difficult;
- intervertebral hernias;
- disability;
- Strong deformation of the joint or the entire limb.
Diagnosis of arthrosis
To make a diagnosis, rheumatologists study the patient's complaints and prescribe an X -ray examination.Most often, radiography is used in 2 projections.The doctor looks at the presence of dystrophic disorders in hyaline cartilage and bone joints.If the articular gap is reduced, the bones are deformed or flattened, there are cystic formations on the surface of the cartilage, osteophytes are obvious signs of arthrosis.During the inspection, arthrosis indicates the instability of the joint: the axis of the limbs and subluxation is disturbed.
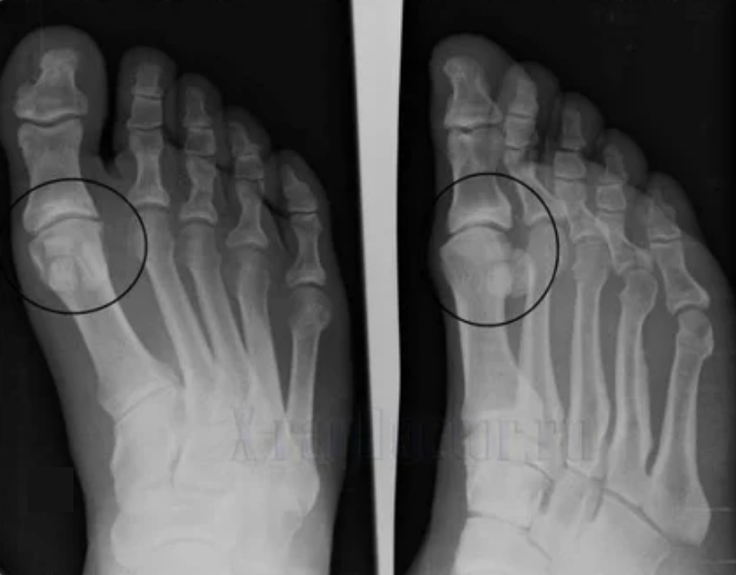
Often an X -ray picture is not able to give complete information about the condition of the joint.For a more thorough study, computed tomography is prescribed, it is effective for examining bones.MRI is more often used to study soft tissues.
During the diagnosis, the involvement of other specialists is practiced who will help determine the root cause of the pathology.Often resort to consultation of a hematologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, orthopedic.
Modern treatment
There are hundreds of ways of arthrosis therapy, but they all come down to a number of methods:
- Drug treatment.The main task is to combat symptoms and prevent further development of a violation.Most often, analgesics are used to relieve pain, non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs to combat inflammation, hormonal drugs are prescribed for severe pain and acute inflammation.Each course is based on chondroprotectors that protect cartilage fabrics from destruction, natural substances are used for their manufacture;
- physiotherapy.Enhances the effectiveness of drugs, fights with inflammation, relieves symptoms, accelerates tissue regeneration.Most often used ultrasonic, electric, magnetic, laser therapy.This also includes mud baths, applications with natural materials, radon baths;
- Medical physical education.It is useful both as a prevention and facilitating the condition.After the correct physical exercises, it is possible to completely eliminate the pain.It is useful to visit the pool, engage in yoga and often walk;
- Manual therapy, massage will help in the treatment of the disease, as they contribute to the prevention of curvature of the joints.After injuries, the manual therapist is able to level the joint, preventing his fixation in the wrong position.After massage, muscle tone is enhanced, blood circulation is accelerated;
- Proper nutrition.A healthy diet will help to enrich the body with nutrients for cartilage and reduce body weight.A large mass increases the wear of the joints;
- Sanatorium-resort treatment will strengthen the joints.In the framework of healing, sanatoriums are offered balneotherapy, exercise therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, etc.;
- Non -traditional therapy.For the treatment of arthrosis, huts, naturo-, aph- and herbal medicine, as well as acupuncture and various folk recipes are used;
- Surgical intervention is the only way to return to the usual life at the third stage of the disease.Endoprosthetics allows you to replace the patient cartilage with the implant.The only drawback of the operation is the high cost.One procedure is enough for 15-20 years.
Preventive measures
So that the arthrosis of the joint does not bother in old age, stands:
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- prevent strong loads;
- observe a diet;
- exclude bad habits;
- Perform gymnastics daily;
- Follow the weight.
Arthrosis is a dangerous disease that is much easier to prevent than cure.With timely seeking a doctor and compliance with the rules of treatment, the patient will be able to maintain a familiar lifestyle for a long time.The lack of therapy and self -medication provoke the rapid aggravation of the disease, and ultimately disability.























